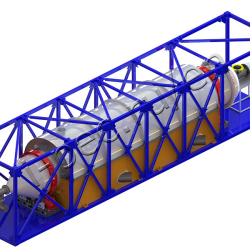
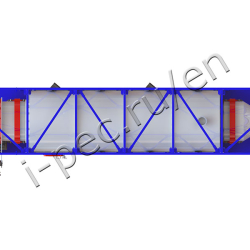
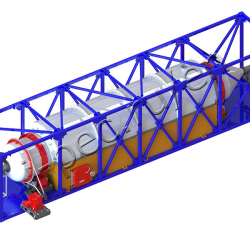
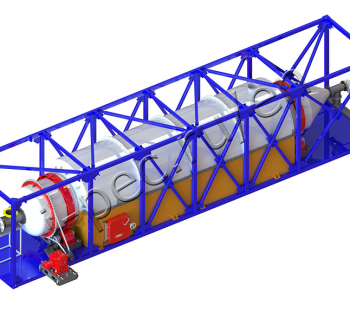
Thermal Decomposition Plant TDP-2-1000R (rotating reactor)
Technical characteristics
1000 kg/h capacity
continuous operation batches per day
60 kWh power consumption
380 voltage
-
ADVANTAGES OF TDP-2-1000R
- solution for plastic waste processing: polypropylene (PP), polystyrene (PS), low density polyethylene (LDPE), high density polyethylene (HDPE)
- innovative design and rotation of the furnace provide:
- uniform distribution of the plastic mass over the reactor walls, resulting in more efficient heat transfer and heating of the raw materials
- increased residence time of raw materials in the reactor, which guarantees full completion of the thermal decomposition process and obtaining high quality products at the outlet
- continuous recycling
- high efficiency
- a wide range of options.
The technological process of TDP-2 waste treatment is based on pyrolysis process – a method of controlled thermal decomposition of raw materials to the necessary components, in oxygen free environment. Raw materials processing allows to obtain conditioning products that can be used for their intended purpose.
- pyrolysis gas
- is used to operate the plant, ensuring its autonomy (thus economic efficiency) and independence from external fuel sources
- is directed to power generation equipment to generate electricity (option)
- boiler fuel
- is used for its intended purpose
- is used to produce a gasoline component, diesel fuel (option, requires additional equipment – rectification column)
- can be evaporated to a gaseous state if necessary
- dry residue (hazard class IV) is used for local, construction and reclamation needs
-
Stage 1. Preliminary preparation of raw materials before loading into TDP
1. Raw plastic is fed by a belt conveyor from the warehouse to the shredder.
2. The raw material is fed by a chain conveyor to the press hopper and then to the extruder, where the polymers are preheated and melted to pasty state.Stage 2. Thermal decomposition process
1. The prepared raw materials are fed from the extruder into the rotary reactor, where they are heated in the oxygen-free environment and its thermal decomposition (pyrolysis) starts.Stage 3: Condensation and separation processes
1. The steam-gas mixture from the pyrolysis chamber passes through a system where the gas is cleaned of mechanical particles and heavy components.
2. Then the steam-gas mixture is cooled in a heat exchanger and fed to a gas-liquid separator, where the gas and liquid phases are separated:
– liquid pyrolysis fuel goes into a fuel tank and then into a fuel storage tank (end product tank)
– pyrolysis gas is fed through a demister to a gas drying column where the residual water vapour is separated from the gas.
3. Dry gas passes through the filters to the gas compressor and then is directed to the gas regulating unit, where it is discharged to the burners to maintain the operating mode of the TDP plant;OPTION:
Depending on the customer’s objectives, the following options can be implemented in the plastic processing unit TDP-2-1000:
– Equipping with Capstone gas turbine generator of required power for electricity generation
– Pyrolysis gas excess utilization system
4. Dry carbon residue is continuously removed from rotary reactor by means of automatic ash removal system to ash receiving hopper.Stage 4. Flue gas removal, energy recovery.